Optimal Time for Gathering Asian Pears: Seeking the Ideal Harvest Moment
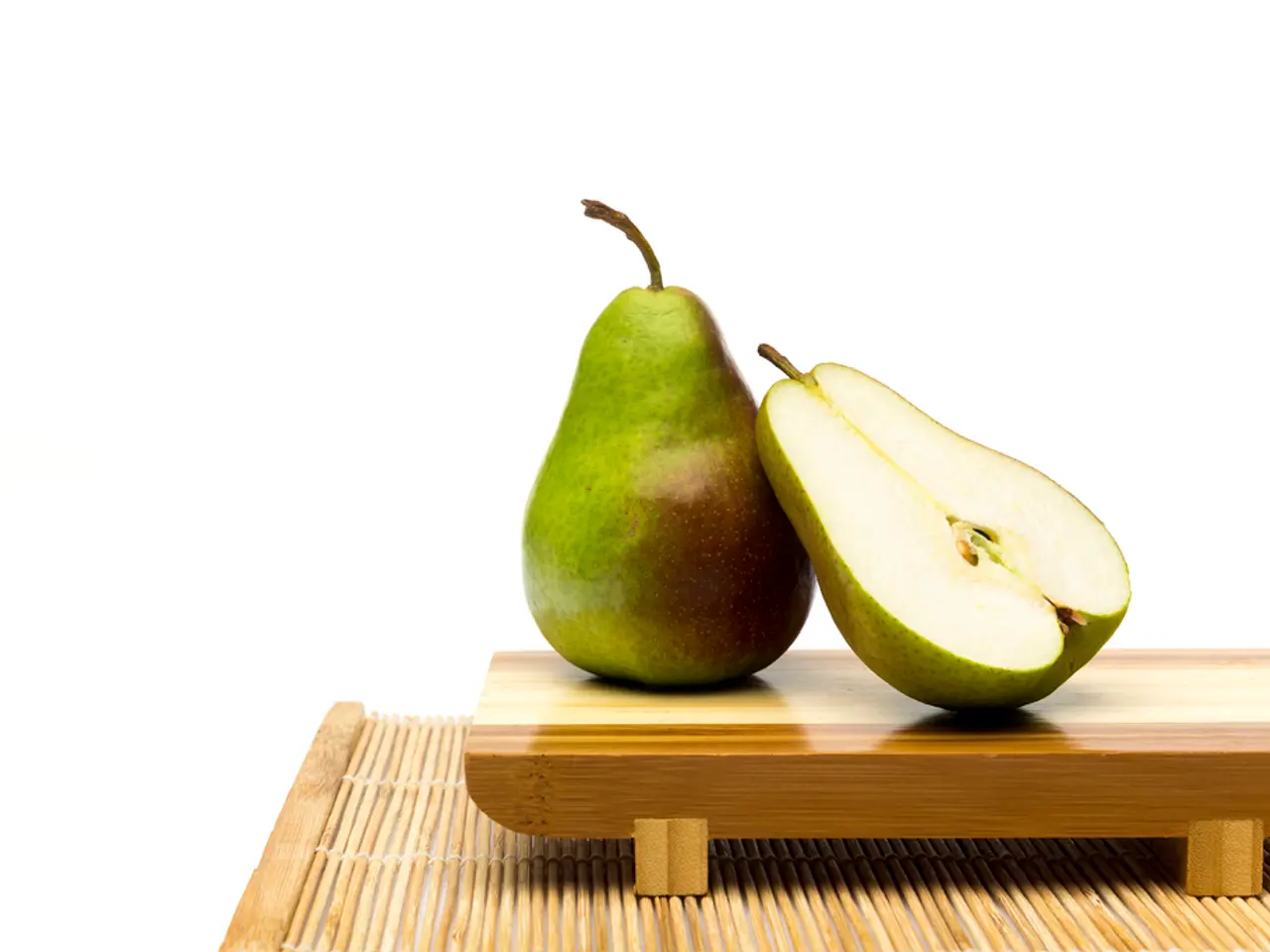
Asian pears, with their delightful blend of sweet and tangy flavors, are a popular addition to many gardens and kitchens. This guide offers best practices for growing, harvesting, and storing these versatile fruits, focusing on popular cultivars, nutritional benefits, and culinary uses.
Growing and Harvesting Asian Pears
Choosing the right cultivar is crucial for growing Asian pears. Nashi pears are sweet and crunchy, ideal for fresh snacking, while Korean pears are preferred in traditional dishes.
Harvesting Asian pears at the right time is essential. They are non-climacteric fruits that do not ripen significantly after picking, so it's important to pick them when they are mature but still firm.
For home growers, ensuring proper bloom-to-harvest intervals and monitoring fruit maturity is key to optimal quality.
Storing Asian Pears
Proper storage is vital for maintaining the freshness and shelf life of Asian pears. Store them in a cool, dry place, ideally between 30°F and 40°F (around -1°C to 4°C), such as a refrigerator or root cellar.
Avoid storing Asian pears near strong-smelling foods, as they absorb odors easily. For ripening pears (if slightly underripe), keep them at room temperature away from direct sunlight but monitor them closely to avoid overripening.
Asian pears can also be frozen, canned, or made into pear syrup for long-term storage.
Popular Cultivars
Popular Asian pear cultivars include the Nashi Pear (Japanese Pear), known for its crisp texture and sweet flavor, and the Korean Pear. Other common cultivars include Anjou, Comice, and Bosc, which are mainly Western pear varieties but are relevant for comparative reference.
Nutritional Benefits
Asian pears are low in calories (~100 calories per 6-ounce serving) and provide a good source of vitamin C and dietary fiber. Their crisp, juicy white flesh combines mild sweetness with nutritional benefits typical of pears.
Culinary Uses
Asian pears can be eaten raw as a crisp, refreshing snack. They are also used in traditional Korean dishes, adding sweetness and texture. They can be prepared by poaching, making pear syrup, or canning for desserts or preserves.
Suitable for freezing after blanching or slicing with lemon to prevent browning, Asian pears are useful for smoothies, baking, or later consumption.
Health Benefits
Asian pears provide 9.9 grams of dietary fiber, which is crucial for digestive health. They also contain vitamins A, C, K, and B6, as well as potassium and magnesium. The antioxidants in Asian pears help reduce the risk of illnesses like cancer and heart disease. Soluble fiber in these pears aids in lowering cholesterol levels.
With their versatility in fresh eating and cooking, combined with good nutritional content, Asian pears are valuable in both home and commercial settings.
[1] Asian Pear Varieties and Cultivation
[2] Asian Pear Preservation
[3] Growing Asian Pears
[4] Nutritional Information for Asian Pears
[5] Storage of Asian Pears